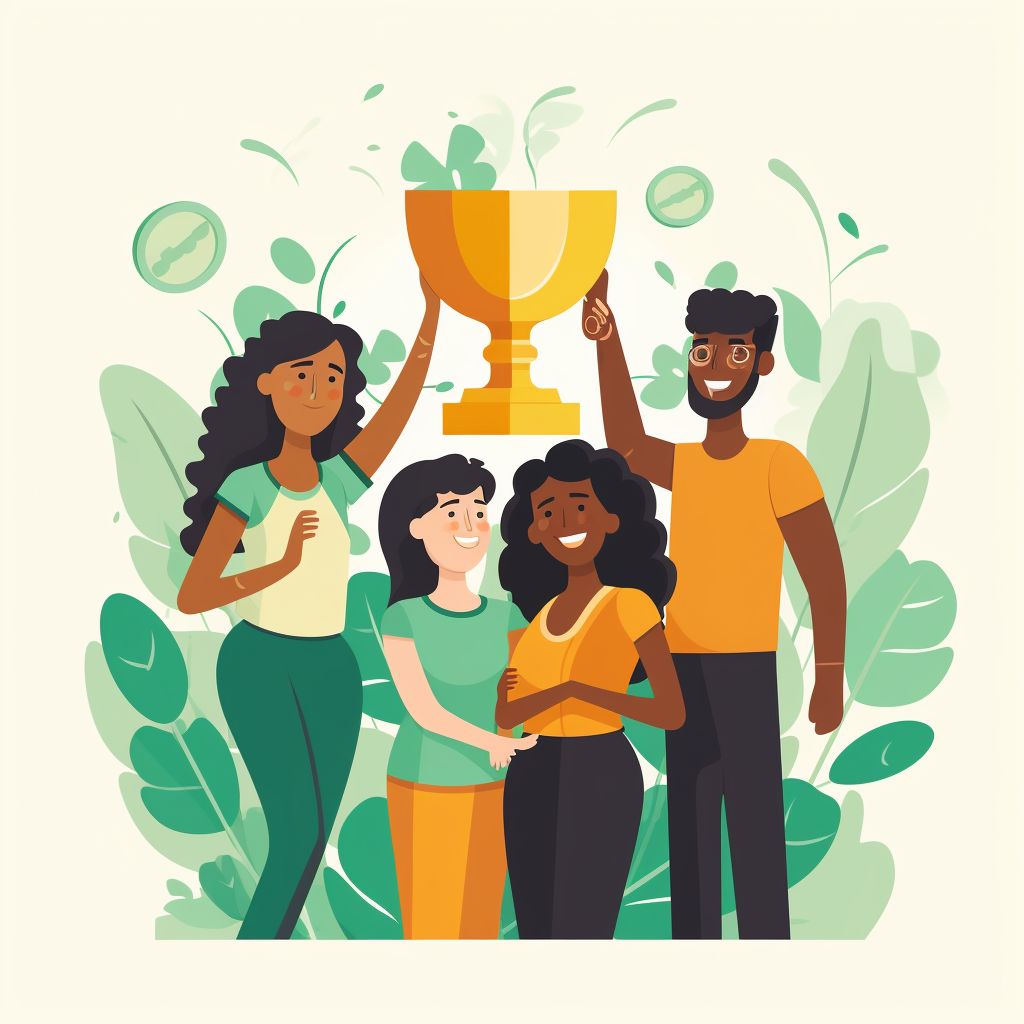
This is how a monarchy begins
Translated from Spanish. View the original post
here
#history The monarchy is one of the oldest forms of government. Its antecedents were chiefdoms or chiefdoms, originated after humanity adopted sedentary life in the Neolithic period, thanks to the invention of agriculture. It was a type of socio-political organization, of a pro-state nature, in which authority and power were centralized in one person or a group of people.
Monarchies emerged with the first civilizations, around 3,000 BC. C., in Mesopotamia, Egypt and the Indus Valley. They consisted of religious governments, in which the monarch was, at the same time, god, priest and military leader.
Among the Jews, the establishment of the monarchy occurred in the eleventh century BC. C. The strong monotheism of this people prevented the deification of the monarch, as happened elsewhere.
In Greece, the monarchy, present in the Mycenaean culture, was replaced from the 8th century BC. C. by aristocratic and democratic forms of government, to be reimplanted under the Empire of Philip of Macedonia and his son Alexander, in the fourth century BC. C.

- Report this post
 Yoors
Premium
Yoors
Premium